Your amazing parathyroid glands
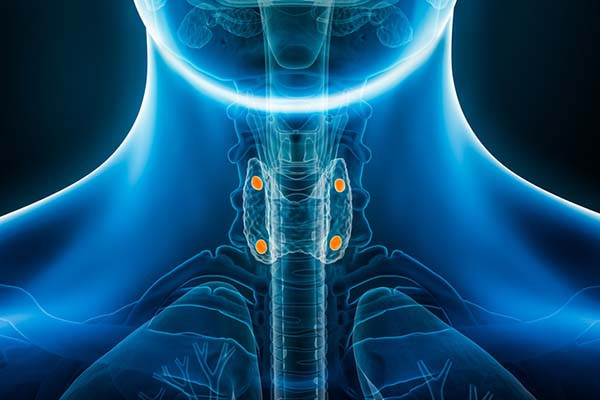

You probably know that you have a thyroid gland. Perhaps you or someone you know has had thyroid tests or a thyroid disorder such as hypothyroidism.
But did you know you also have a parathyroid gland? It’s true — in fact, most people have four of them, even though one would suffice.
Where are the parathyroid glands?
From the name, you might assume the role of the parathyroid glands is related to that of the thyroid gland. Well, you’d be wrong. The name comes solely from their location: they sit just behind the thyroid gland: two on the right side, two on the left.
The parathyroid glands are small (the size of peas), and can weigh less than a thousandth of an ounce each. Although it’s normal to have four parathyroid glands, about 13% of people have fewer and 5% have more. And some people have parathyroid glands in other locations, such as alongside the esophagus or in the chest. This variation rarely matters, unless surgery is necessary to remove one or more of them.
What do the parathyroid glands do?
Logically enough, parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH). And what does PTH do? It has several functions, including:
- Regulating calcium: Calcium is a mineral with many essential roles throughout the body, such as maintaining bone strength, allowing nerves and muscles to function normally, and making sure blood clots as it should. Higher levels of PTH lead to higher calcium levels in the blood through actions on the kidneys and bones.
- Regulating phosphorus: Among other roles, this mineral is a key component of our DNA, bones, and teeth. Phosphorus activates essential enzymes throughout the body, including enzymes necessary for cell reproduction and survival. It also helps with nerve and muscle function.
- Regulating vitamin D: This vitamin is actually a hormone that helps maintain normal levels of calcium throughout the body, by controlling how much gets absorbed from food in the intestinal tract and how much is lost by the kidneys in your urine. Remember PTH? Well, PTH regulates production of the enzyme that converts inactive vitamin D to an active form that helps your gut absorb calcium and reduces the loss of calcium in urine.
PTH released by the parathyroid glands helps keep each of these nutrients in balance. For example, if your blood calcium level falls, your parathyroid glands make more PTH. Higher amounts of PTH prompt bones to release stored calcium into the bloodstream, and also signal the kidneys to pull back on the amount of calcium lost through urine.
What if your blood calcium level rises? Then the parathyroid glands make less PTH, which helps to correct the blood calcium level.
Which diseases involve the parathyroid glands?
The most common are:
- Hyperparathyroidism: This is a condition in which the parathyroid glands make more than the normal amount of PTH. This can be due to a benign or cancerous tumor on a single gland, or due to multiple glands becoming overactive. Or it may be due to some other trigger, such as a low level of calcium in the blood, inadequate vitamin D levels, or kidney failure. When there’s too much PTH, blood calcium levels can become dangerously high and phosphorus levels fall. Surgery may be recommended to remove the overactive gland or glands.
- Hypoparathyroidism: This rare condition is diagnosed when less than the normal amount of PTH is produced. The most common causes are prior neck surgery or radiation, autoimmune disease, or low magnesium levels.
- Parathyroid cancer: Risk factors for parathyroid cancer include certain genetic diseases and prior radiation to the neck.
Why do we rarely hear about the parathyroid glands?
The reason is that most of the time they do their job without fuss or fanfare. Although disorders of the parathyroid glands are not rare, they are just uncommon enough that most people will never hear about them. I think of the parathyroid glands as one of many parts of our bodies that play a huge role in our health, but go unappreciated because they are so good at what they do.
Many other quiet heroes, including the thymus gland, serve as testaments to the remarkable design and function of the human body. Then again, I can think of a few body parts that could be considered expendable.
The bottom line
I hope it’s comforting to know that your amazing parathyroid glands are keeping tabs on your calcium levels and helping your bones, nerves, muscles, and other organs to function normally.
Ounce for ounce, the parathyroid glands may be the most important glands you’d never heard of. Until now.
About the Author

Robert H. Shmerling, MD, Senior Faculty Editor, Harvard Health Publishing; Editorial Advisory Board Member, Harvard Health Publishing
Dr. Robert H. Shmerling is the former clinical chief of the division of rheumatology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), and is a current member of the corresponding faculty in medicine at Harvard Medical School. … See Full Bio View all posts by Robert H. Shmerling, MD








 Each year, more than 4.5 million dog bites occur in the United States. Despite what you might assume, most of these incidents don’t happen when an unfamiliar dog attacks someone in a park or another outdoor location. Instead, most dog bites are inflicted by a pet dog in a home.
Each year, more than 4.5 million dog bites occur in the United States. Despite what you might assume, most of these incidents don’t happen when an unfamiliar dog attacks someone in a park or another outdoor location. Instead, most dog bites are inflicted by a pet dog in a home.